FSc Chemistry 12th Ch 15 Common Chemical Industries in Pakistan Exercise Short Questions
FSc Notes Part II, 2nd year Chemistry Notes, Short Questions, Book Exercise SQs, MCQs, Quizzes, Long Questions, Numerical, TCA Notes, tcanotes, The Concept Academy Notes
If you want to view other Ex SQs / MCQs / Quizzes / Long Qs of FSc Chemistry Part 2 Please Click Here.
Exercise Short Questions
Q4 What are phosphatic fertilizers. How are they prepared? Mention the role of phosphorus in the growth of plants.
Ans. Phosphatic Fertilizers
These fertilizers provide phosphorus to the plants or soil. Phosphorus is required to stimulate early growth to accelerate the seed and fruit formation during the later stages of growth. It also increases resistance to diseases. The various phosphatic fertilizers have different compositions, due to which they have different solubilities. The two most important water soluble fertilizers are super phosphate (calcium super phosphate) Ca(H2P4)2and triple phosphate (diammonium- phosphate (NH4)2HPO4).
(i) Diammonium Phosphate (NH4)2HPO4
This compound of fairly high purity is prepared by continuous process that consists of reacting anhydrous ammonia gas and pure phosphoric acid at 60 – 70 °C and pH 5.8 – 6.0.
NH3 (g) + H3PO4 (l) → (NH4)2HPO4 + heat
It is an exothermic reaction. The heat of reaction vaporizes water from the liquor and the crystals of diammonium phosphate are taken out, centrifuged, washed and dried. It contains 16% nitrogen and 48% P2O5. This product contains about 75% plant nutrients and is deemed suitable for use either alone or in mixed with other fertilizers.
Q5. (a) What are fertilizers? Why are they needed?
Ans. Fertilizers are the substances added to the soil to make up the deficiency of essential elements like nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium (NPK) required for the proper growth of plants. Fertilizers enhance the natural fertility of the soil or replenish the chemical elements taken up from soil by the previous crops.
Q5. (b) Discuss the classification of fertilizers and their uses.
Ans. Classification of Fertilizers
Fertilizers are classified according to the nature of the elements like nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium which they provide to the soil. This classification gives the following types of fertilizers.
- Nitrogenous fertilizers
- Phosphatic fertilizers
- Potassium fertilizers
1. Nitrogenous Fertilizers
These fertilizers supply nitrogen to the plants or soil. Nitrogen is required during the early stage of plant growth for the development of stems and leaves. It is the main constituent of protein, imparts green colour to the leaves and enhance the yield and quality of the plants. Some of the examples of nitrogen fertilizers are: – ammonium sulphate, calcium ammonium nitrate, basic calcium nitrate, calcium cyanamide, ammonia, ammonium nitrate, ammonium phosphate, ammonium chloride and urea.
2. Phosphatic Fertilizers
These fertilizers provide phosphorus to the plants or soil. Phosphorus is required to stimulate early growth to accelerate the seed and fruit formation during the later stages of growth. It also increases resistance to diseases. The various phosphatic fertilizers have different compositions, due to which they have different solubilities. The two most important water soluble fertilizers are super phosphate (calcium super phosphate) Ca(H2PO4)2and triple phosphate (diammonium- phosphate (NH4)2HPO4).
3. Potassium Fertilizers
These fertilizers provide potassium to the plant or soil. Potassium is required for the formation of starch, sugar and the fibrous material of the plant. They increase resistance to diseases and make the plants strong by helping in healthy root development. They also help in ripening of seeds, fruits and cereals. Potassium fertilizers are especially useful for tobacco, coffee, potato and corn.
Q5. (c) How is urea manufactured in Pakistan? Describe in detail the process used.
Ans. Urea (NH2-CO-NH2)
Urea is a high quality nitrogenous fertilizer. It contains about 46% nitrogen and is the most concentrated solid nitrogen fertilizer. It is the most widely used nitrogen fertilizer in Pakistan.
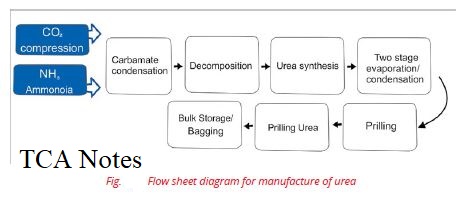
Manufacturing Process
Urea is produced by the reaction of liquid ammonia with gaseous carbon dioxide.
Following steps are involved in the manufacture of urea.
- Preparation of Hydrogen and Carbon dioxide
- Preparation of Ammonia
- Preparation of Ammonium Carbamate
- Preparation of Urea
- Concentration of Urea
- Prilling
iii. Preparation of Ammonium Carbamate
Gaseous CO2 is mixed with ammonia in the volume ratio of 1:2 in a reactor to produce ammonium carbamate.

iv. Preparation of Urea
Dehydration of ammonium carbamate gives urea.
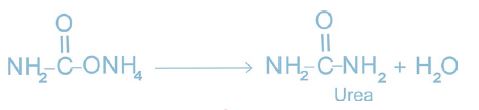
v. Concentration of Urea Solution
The urea solution is concentrated in an evaporation section where water is evaporated by heating with steam under vacuum in two evaporation stages whereby 99.7% urea melt is obtained. It is then pumped to prilling tower.
vi. Prilling
The molten urea is sprayed at the prilling tower by means of prilling bucket where it is cooled by the air rising upward. Molten droplets solidify into the form of prills. Urea prills thus produced are either sent to the bagging section or to the bulk storage, Fig.
Q6. (a) What are the prospects of fertilizer industry in Pakistan?
Ans. Fertilizer Industry in Pakistan
Pakistan is essentially an agricultural country. In order to keep up the production of agricultural commodities and to compensate for the depletion of nutrients which get exhausted by repeated cultivation, the urea fertilizer has gained importance.
For a developing country like Pakistan, there is an ever-growing demand for urea fertilizer. Government of Pakistan is trying its utmost to narrow the gap between supply and demand of fertilizers. Consistent efforts have been made to install fertilizer manufacturing plants. At present, there are about 14 fertilizer plants in private as well as public sectors in the country which are manufacturing different types of fertilizers.
The total production of urea fertilizer in 2002 in Pakistan is about 56,30,100 metric tons/annum.
Q6. (b) What are essential nutrient elements and why these are needed for plant growth?
Ans. Elements Essential for Plant Growth
Plants need nutrients from the soil for a healthy growth. The elements essential for the plant growth can be classified as micro-nutrients and macronutrients.
i. Micro-nutrients (Trace elements)
The nutrients which are required in a very small amount for the growth of plant, are called micro-nutrients. These include Boron, Copper, Iron, Manganese, Zinc, Molybdenum and Chlorine.
Only minute amounts of these elements are needed for healthy plant growth and it may be dangerous to add too much quantity because they are poisonous in larger quantities. These are generally
required in quantities ranging from 6 grams to 200 grams per acre.
ii. Macro-nutrients
The nutrients which are required in a large amount for the growth of plants, are called macro-nutrients. These include Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium, Calcium, Magnesium, Sulphur, Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen. These are generally required in quantities ranging from 5 kg to 200 kg per acre.
Q6. (c) Write down the essential qualities of a good fertilizer?
Ans. Essential Qualities of a Good Fertilizer
The essential requisites of a good fertilizer are:
- The nutrient elements present in it must be readily available to the plant.
- It must be fairly soluble in water so that it thoroughly mixes with the soil.
- It should not be injurious to plant.
- It should be cheap.
- It must be stable so that it is available for a longer time to the growing plant.
- It should not alter the pH of the soil.
- By rain or water, it should be converted into a form, which the plant can assimilate easily.
Q7. (a) Describe the composition of a good portland cement.
Ans. The important raw materials used for the manufacture of cement are:
- Calcarious material (limestone, marble, chalks, marine shell) as source of CaO.
- Argillaceous material (clay, shale, slate, blast furnace slag) They
provide acidic components such as aluminates and silicates, - Other raw material being used is gypsum.
An average composition of a good sample of Portland cement is as
follows:
| Compound | Percentage |
| Lime (CaO) | 62 |
| Silica (SiO2) | 22 |
| Alumina (Al2O3) | 7.5 |
| Magnesia (MgO) | 2.5 |
| Iron oxide (Fe2O3) | 2.5 |
| Sulphur trioxide (SO3) | 1.5 |
| Sodium oxide (Na2O) | 1.0 |
| Potassium (K2O) | 1.0 |
Q7. (b) Discuss the wet process for the manufacturing of cement with the help of flow sheet diagram.
Ans. Wet Process: In this process grinding is done in the presence of water. There are five stages in the manufacture of Portland cement Fig.
- Crushing and grinding of the raw material.
- Mixing the material in correct proportion.
- Heating the prepared mixture in a rotary kiln.
- Grinding the heated product known as clinker.
- Mixing and grinding of cement clinker with gypsum.
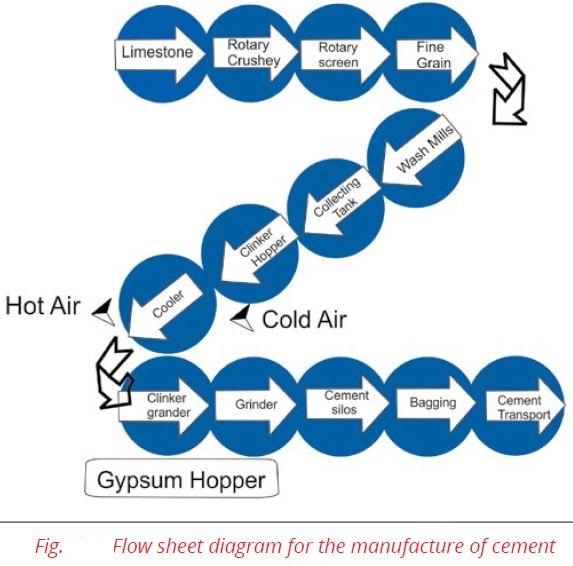
1. Crushing and Grinding
Soft raw materials are first crushed into a suitable size, often in two stages, and then ground in the presence of water, usually in rotating cylindrical ball or tube mills containing a charge of steel balls.
2. Mixing of Raw Material
The powdered limestone is then mixed with the clay paste in proper proportion (limestone 75%, clay 25%); the mixture is finely ground and made homogeneous by means of compressed air mixing arrangement. The resulting material is known as slurry.
The slurry, which contains 35 to 45% water, is sometimes filtered to reduce the water content from 20 to 30% and the filler cakes are stored in storage bins. This reduces the fuel consumption for heating stage.
3. Heating the Slurry in a Rotary Kiln
Raw meal or slurry prepared as above is introduced into the rotary kiln with the help of a conveyer. The rotary kiln consists of a large cylinder 8 to 15 feet in diameter and 300-500 feet in length. It is made of steel and is lined inside with firebricks. The kiln rotates horizontally on its axis at the rate of 1-2 revolution per minute and it is inclined a few degree.
As the kiln rotates, the charge slowly moves downward due to the rotary motion.
Now the charge is heated by burning coal, oil or natural gas. In the rotary kiln the charge passes through the different zones of temperature where different reactions take place. The charge takes 2-3 hours to complete the journey in the kiln.
(a) Drying or Pre-heating Zone (Minimum temperature zone)
In this zone the temperature is kept at 500°C, whereby the moisture is removed and the clay is broken into Al2O3, SiO2, and Fe2O3.
(b) Decomposition Zone (Moderate temperature zone)
Here the temperature goes upto 900°C In this zone the limestone (CaCO3) decomposes into lime (CaO) and CO2.
CaCO3 (s) –9oooC→ CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
(c) Burning Zone (Maximum tem perature zone)
In this zone, the temperature goes up to 1500°C and the oxides, e.g. CaO, SiO2, Al2O3 and Fe2O3 combine together and form calcium silicate, calcium aluminate and calcium ferrite.
(d) Cooling Zone
This is the last stage in the kiln where the charge is cooled up to 150-200°C
4. Clinker Formation
The resulting product obtained from the kiln is known as cement clinker. This has the appearance of greenish black or grey coloured balls varying in size from small nuts to peas.
5. Grinding the Clinkers with Gypsum
The cement clinkers are then air-cooled. The required amount of gypsum (2.0%) is first ground to a fine powder and then mixed with clinkers. At this stage finished cement is pumped pneumatically to storage silos from where it is drawn for packing in paper bags or for dispatch in bulk containers.
Q7. (c) What do you understand by the term “setting of cement”. Also discuss the reactions taking place in first 24 hours?
Ans. Setting of Cement
The use of cement in the construction of building is based on its property of setting to a hard mass when its paste with water is allowed to stand for sometime. The reactions involved in the setting of cement are described as follows:
i. Reactions Taking Place in First 24 Hours.
A short time after the cement is mixed with water, tri-calcium aluminate absorbs water (hydration) and forms a colloidal gel of the composition, 3Ca. Al2O3.6H2O, (hydrated tricalcium aluminate).
This gel starts crystallizing slowly, reacts with gypsum (CaSO4.2H2O) to form the crystals of calcium sulpho-aluminate (3CaO.Al2O3.3CaSO4.2H2O).
Q8. What are the essential non-woody raw materials used in the production of pulp and paper in Pakistan?
Ans. The list of non-woody raw materials used in the production of pulp and paper in Pakistan is as following:
| i. Wheat straw | ii. Rice straw | iii. Bagasse |
| iv. Bamboo | v. Rag | vi. Cotton stalk |
| vii. Cotton linter | viii. Kahi grass | ix. Grasses |
Q9 (a) What are the principal methods of chemical pulping used for the production of paper?
Ans. The following are three principal methods of chemical pulping and are used for the production of paper pulps:
- Kraft process (Alkaline)
- Sulphite process
- Neutral sulphite semi-chemical process (NSSC)
Q9. (b) Describe the neutral sulphite semi-chemical process for the manufacturing of pulp and paper.
Ans. Neutral Sulphite Semi Chemical Process
Process Description
This process utilizes sodium sulphite cooking liquor which is buffered with sodium carbonate or NaOH to neutralize the organic acid liberated from the raw materials.
The non-woody raw materials which are used in this process are wheat straw, rice straw, bagasse, cotton linter and rags. Wheat straw may be used alone or combined with other materials in different proportions. The essential steps in the process are as follows in Fig.
- Cutting of the raw materials
- Dry cleaning
- Wet cleaning
- Screening
- Digestion
- Blow tank
- Pulp washing
- Bleaching
- Paper making machine
- Stock preparation plant
i. Cutting of Raw Materials
The non-woody raw materials come in the precut state and are processed as such. But in the case of wood based raw materials, big logs are cut into small chips before further processing.
ii. Dry Cleaning
Wheat straw is collected from the storage and is then sent for dry cleaning. For this purpose air is blown into the raw material, which removes unwanted particles.
iii. Wet Cleaning
Dry wheat straw is then subjected to wet cleaning, which not only removes the remaining dust particles, but the soluble materials also get dissolved in water.
iv. Screening
In most pulp and paper processes some type of screening operation is required to remove the over sized troublesome and unwanted particles. Magnetic separator removes iron pieces like nails and bolts, etc. Stones and other oversized pieces are removed by centri-cleaners. The major types of chest screens are vibratory, gravity, and centrifugal. The material is then sent to wet silo.
v. Digestion
From wet silo, the material is sent to digester. The digester is usually 10 meters in length and 2 meters in diameter. It is made of steel and wrought iron. This is the main unit of the process. The digestion process can be either batch or continuous. In our country batch process is mostly used.
As the raw material enters into the digester, steam is introduced at the bottom and a liquor containing sodium sulphite is injected simultaneously to cover the raw material. Sodium sulphite used is buffered with sodium carbonate or sodium hydroxide to maintain its pH 7-9. The digester is closed carefully. It is revolved at 2.5 RPM and a temperature of 160- 180°C is maintained.
The digester takes 45 minutes to attain the desired temperature after which it gets switched off automatically and pressure is released.
vi. Blow Tank
The cooked material from the digester is blown into a blow tank and then pumped to a centrifugal screen for the separation of cooked from uncooked materials.
vii. Pulp Washing
The cooked material from the blow tank is washed thoroughly with water using 80- mesh sieve to remove the black liquor that would contaminate the pulp during subsequent processing steps. The pulp is washed with required amount of water to remove soluble lignin and coloured compounds. Lignin is an aromatic polymer and causes paper to become brittle. It is then thickened and finally stored in high-density storage tower.
viii. Bleaching
The pulps obtained from chemical pulping are brown in colour and are unsuitable for printing and writing papers which require a bright white pulp. The colour of these pulps is mainly due to residual lignin. These pulps are then sent to bleaching unit.
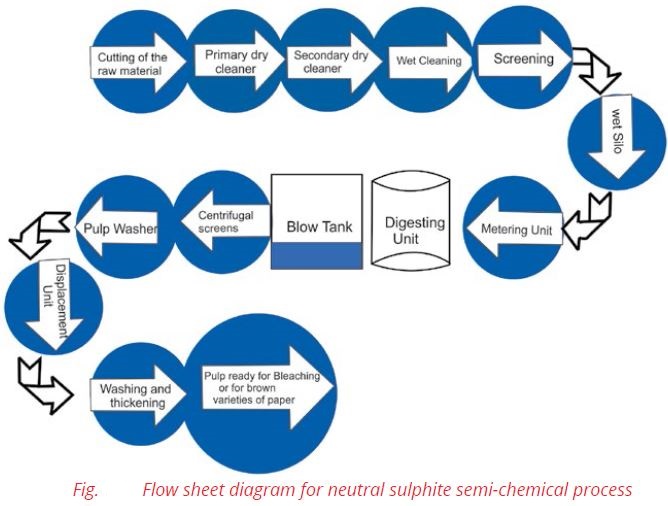
In Pakistan, bleaching is done with chlorine or sodium hypochlorite and hydrogen peroxide. After washing, the unbleached pulp is sent to the chlorinator where chlorine at 4 – 5 bar pressure is injected from chlorine tank. The chlorine react with unbleached pulp at about 45°C for 45-60 minutes to give the good results. The residual chlorine is neutralized with water which act as antichlor. The correct dosage is important and calculated amount of chlorine is needed to achieve the required brightness. After chlorination pulp is washed with hot water at 60°C and is then sent to the storage tank. Pulp is dried with hot air supply. After drying the pulp is ready for manufacturing of paper.
ix. Stock Preparation Plant
There are three important stages in the treatment of the pulp prior to its delivery to the paper making machine. The first is the dispersion of the pulp as a slurry in water, the second is the mechanical refining or beating of the fibres to develop appropriate physical and mechanical properties for the product being made and the third is the addition of chemical additives end recycled fibres from the waste paper plant. Wet end chemistry of paper start from here.
x. Paper Making Machine
A basic Fourdrinier type machine is used for paper making and a brief description of its major components is given below Fig.
(a) Flow Spreader: The flow of spreader takes the plup and distributes it evenly across the machine from back to front. Consistency of the stock is below 1%.
(b) Head Box: The pressurized head box discharges a uniform jet of pulp suspension on a fabric where special suction devices work for the removal of water.
(c) Fourdrinier Table: The endless, moving fourdrinier fabric forms the fibre into a continuous matted web while the fourdrinier table drains the water by suction forces.
(d) Press Section: The paper sheet is conveyed through a series of roll presses where additional water is removed and the web structure is consolidated (i.e the fibres are forced into intimate contact).
(e) Dryer Section: Wet sheet of paper so formed is dried in the dryer section of the machine with the help of rotary drum. Water is separated from the fibre either by gravity, by suction or by pressing and by heating.
(f) Calendar Stock: The sheet is calendered through a series of roll nips to reduce thickness and smooth the surface.
(g) Reel: The dried paper is wound in the form of a reel having final moisture of about 6-8%.

Q10 (a) What are the common bleaching agents used in paper industry in Pakistan? Briefly describe the bleaching process.
Ans. The common bleaching agents used in paper industry in Pakistan are chlorine dioxide (ClO2). Sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Chlorine gas is also use for this purpose.
Bleaching
In Pakistan, bleaching is done with chlorine or sodium hypochlorite and hydrogen peroxide. After washing, the unbleached pulp is sent to the chlorinator where chlorine at 4 – 5 bar pressure is injected from chlorine tank. The chlorine react with unbleached pulp at about 45°C for 45-60 minutes to give the good results. The residual chlorine is neutralized with water which act as antichlor. The correct dosage is important and calculated amount of chlorine is needed to achieve the required brightness. After chlorination pulp is washed with hot water at 60°C and is then sent to the storage tank. Pulp is dried with hot air supply. After drying the pulp is ready for manufacturing of paper.
Q10. (b) What are the prospects of paper industry in Pakistan?
Ans. Paper Industry in Pakistan
Paper plays such an important role in the present day economic development that its consumption is taken as an index of a country’s progress and prosperity. There was no pulp and paper industry in Pakistan at the time of independence in 1947.The country consumed about 25000 tons of pulp and paper products per year and all of these were imported from abroad at a cost of 25 million rupees. The start of the paper industry in our country was very slow because of various reasons, amongst the major ones being the non-availability of suitable fibrous raw material.
Due to high prices of paper in Pakistan its per head consumption is among the lowest in the world. Paper consumption in Pakistan is around 5 kg per person per year.
To make our country self-sufficient in this important commodity, we must utilize every source of raw material like non-woody and woody. Fortunately, Pakistan has enough source of non-woody material, which in future can meet the requirements of our pulp and paper industry. The efforts are being made to install more pulp and paper industries in the country.
At present there are more than 30 pulp and paper industries in private as well as in public sectors, which are manufacturing pulp and paperboard.
MCQs / Quiz
Additional Short Questions

Q1. Why prilled urea is more better than a fine powder?
Ans. The conversion of urea into granules in called prilling. Prilled urea spread on crops more easily than a fine powder. Powder can stay at leaves of plants while granules do not.
Q2. Ammonium nitrate is not useful fertilizers for paddy rice, why?
Ans. Paddy rice requires greater quantity of water. Microbial bacteria in flooded fields decompose ammonium nitrate into nitrogen gas.
Q3. Which crops require more potassium fertilizers?
Ans. Tobacco, coffee, potato and corn require more potassium fertilizers.
Q4. Which raw materials are used for cement?
Ans. Important raw materials for cement industry are
- calcarious material; limestone, marble, chalk marine shells
- argillaceous materials, clay, shale, slate.
- gypsum
Q5. Why we call cement as Portland cement?
Ans. In 1824, Joseph Aspdin prepared cement by heating limestone and clay. When it is mixed with water it changes to a hard mass. This hard mass has resemblance with the stones of a famous building material obtained from island of Portland near England.
Q6. Is cement a mixture or compound?
Ans. Cement is a mixture of many compounds and each compound has its own characteristics properties. Final properties of cement depends upon the composition of cement.
Q7. Which process is used for the manufacturing of cement in Pakistan?
Ans. There are two manufacturing processes for cement
- dry process
- wet process
Choice of dry or wet process depends upon the physical conditions of raw materials, local climatic condition of factory. and fuel prices. In the Pakistan mostly wet process is used. Wet process is free from dust, grinding is easier and composition of cement can easily by controlled.
Q8. Write the name of different zones and their temperature in rotary kiln?
Ans. There are four zones:
- Drying zone (500°C)
- Decomposition zone (800°C)
- Burning zone (1500°C)
- Cooling zone (150- 200°C)
Q9. What are clinkers?
Ans. The product obtained from the rotary kiln is known as clinker. They are greenish black or grey coloured balls varying in size from small nuts to peas. This clinker is mixed with 4 to 5% gypsum and finally ground product is called cement.
Q10. Write the names of woody raw materials for pulp making?
Ans. Woody materials are poplar, eucalyptus and fur.
Q11. What is the role of additives in paper making?
Ans. Additives increase the mechanical strength of paper and reduces the pores of the paper. They increase the glaze of the paper.
Q12. What is the role of head box in paper making, Fourdrinier machine?
Ans. Head box discharges a uniform jet of pulp suspension on a fabric. Water of pulp is removed.
Q13. What is calendaring in paper making?
Ans. Size of paper sheet is reduced in thickness by the help of nip rolls. Surface of thepaper becomes smooth and pores are reduced. This process is called calendering.































